Poster
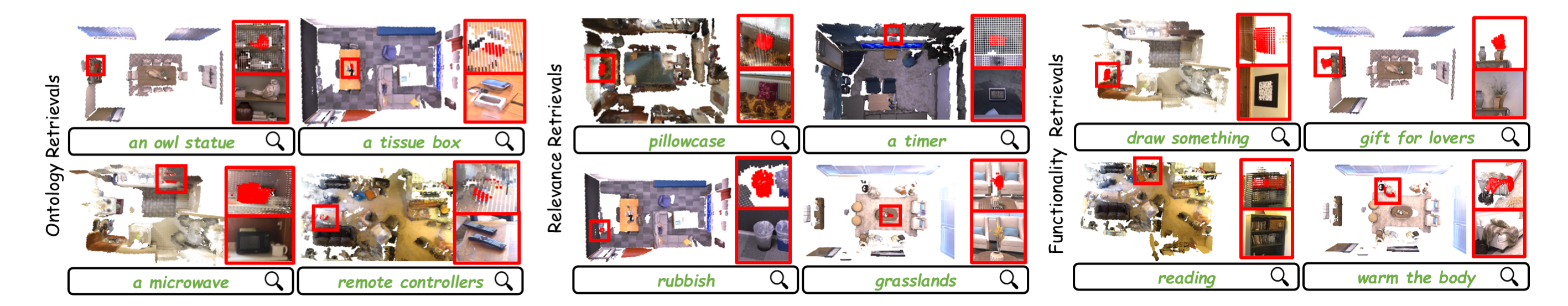
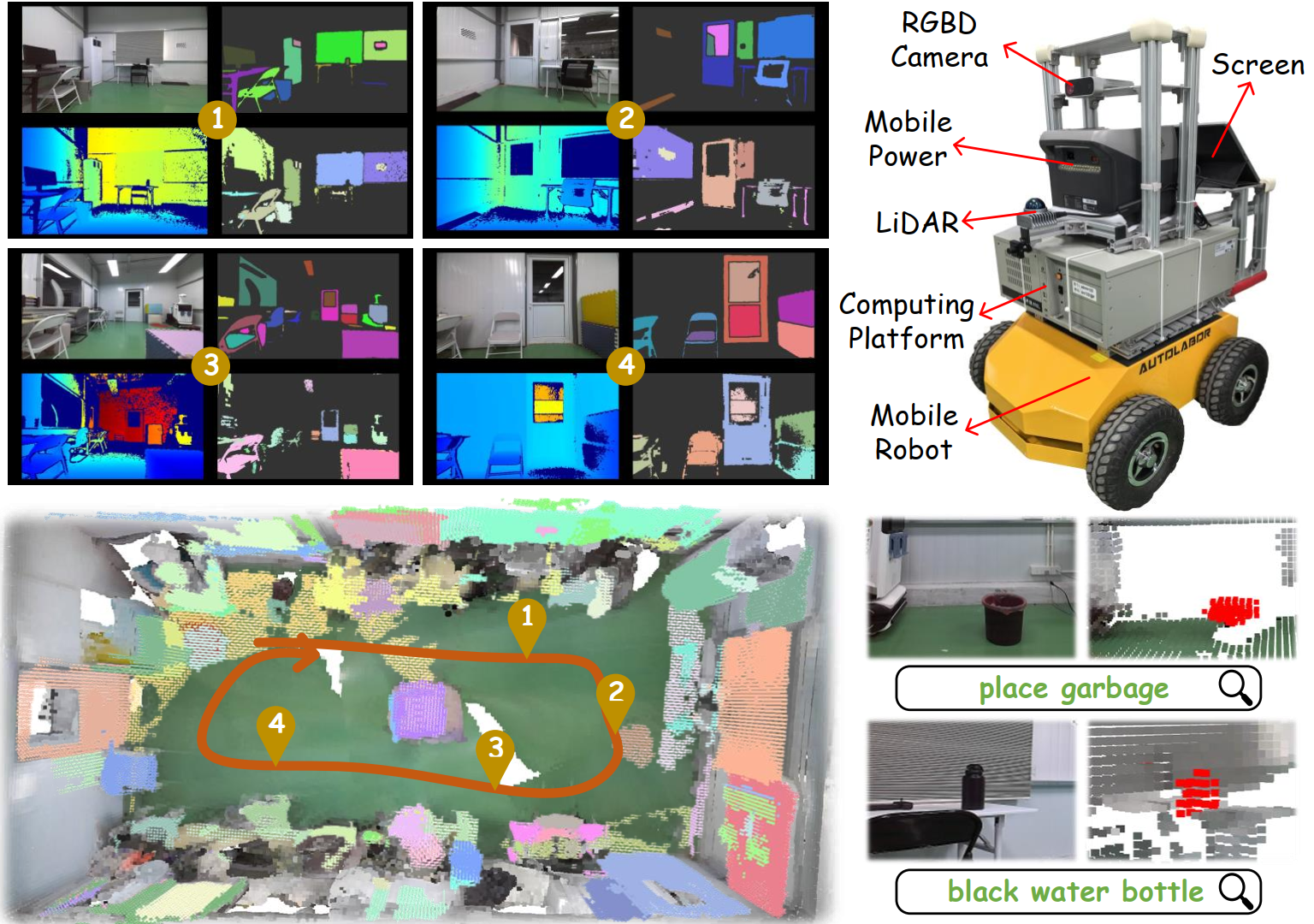
In recent years, vision-language models (VLMs) have advanced open-vocabulary mapping, enabling mobile robots to simultaneously achieve environmental reconstruction and high-level semantic understanding. While integrated object cognition helps mitigate semantic ambiguity in point-wise feature maps, efficiently obtaining rich semantic understanding and robust incremental reconstruction at the instance-level remains challenging. To address these challenges, we introduce OpenVox, a real-time incremental open-vocabulary probabilistic instance voxel representation. In the front-end, we design an efficient instance segmentation and comprehension pipeline that enhances language reasoning through encoding caption. In the back-end, we implement probabilistic instance voxels and formalize the cross-frame incremental fusion process into two subtasks: instance association and live map evolution, ensuring robustness to sensor and segmentation noise. Extensive evaluations across multiple datasets demonstrate that OpenVox achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, and open-vocabulary retrieval. Furthermore, real-world robotics experiments validate OpenVox's capability for stable, real-time operation.
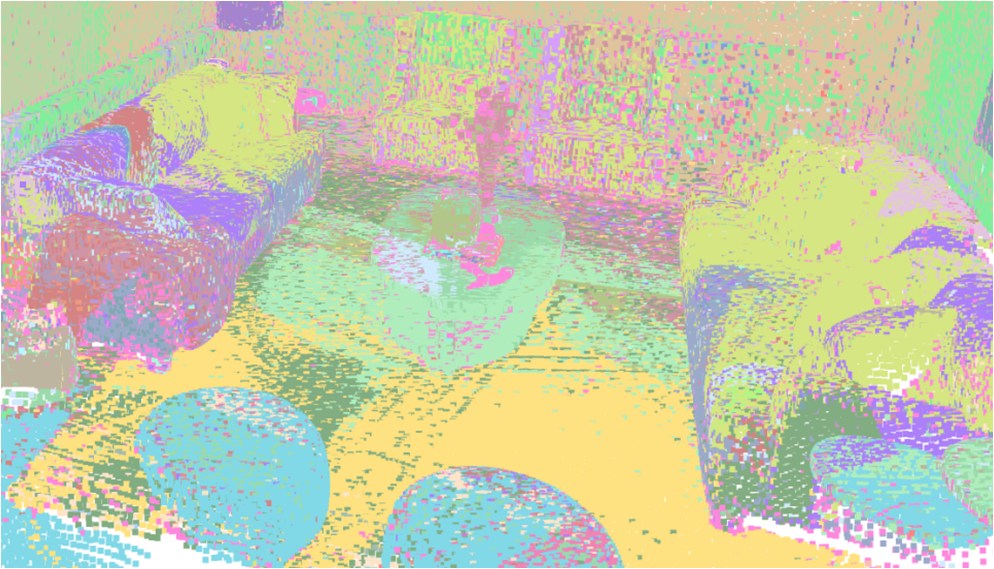
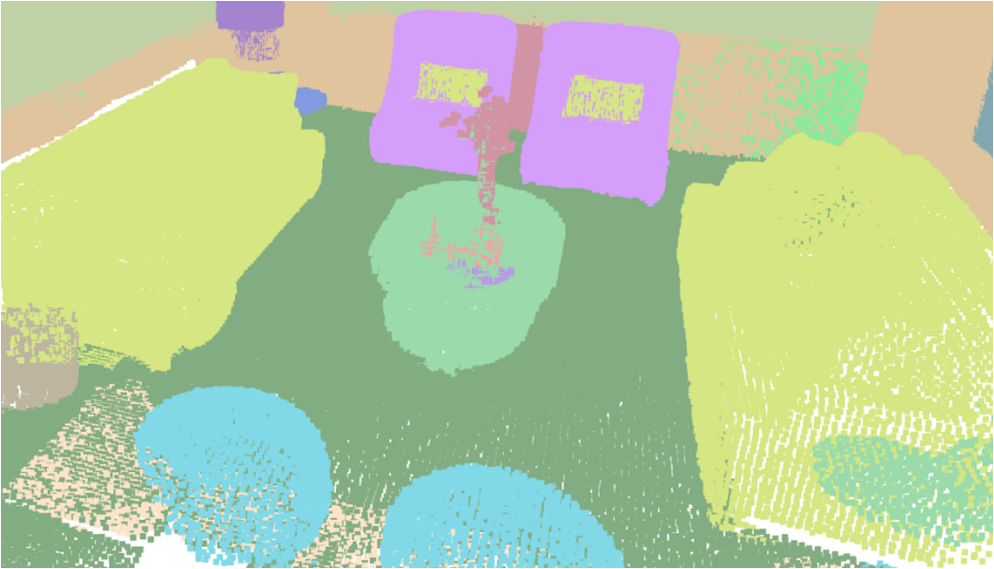
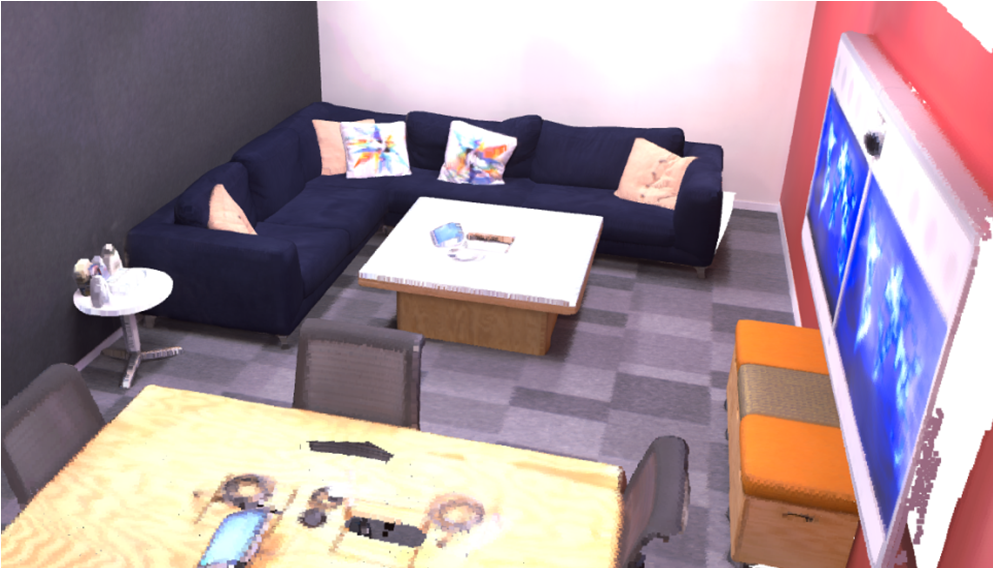
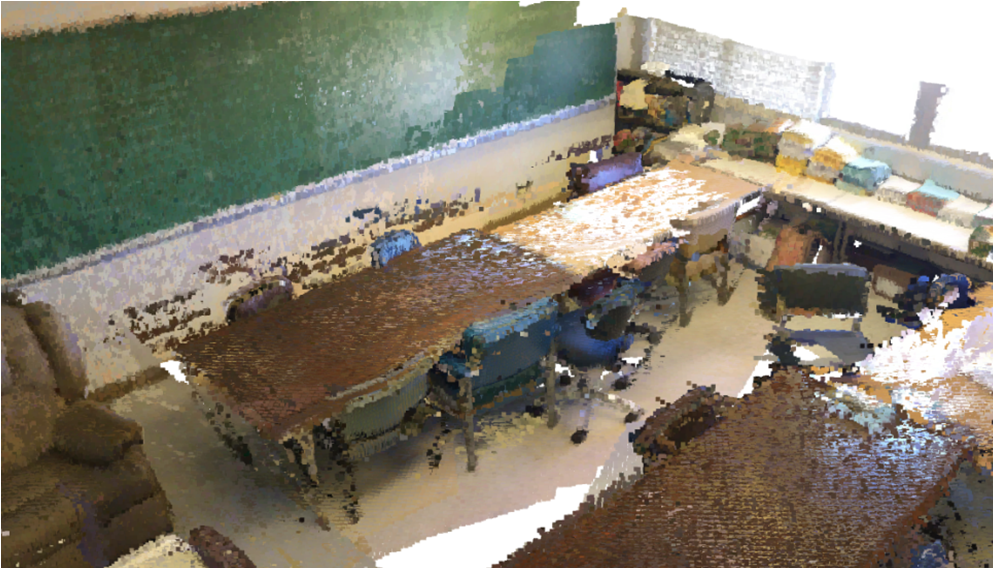
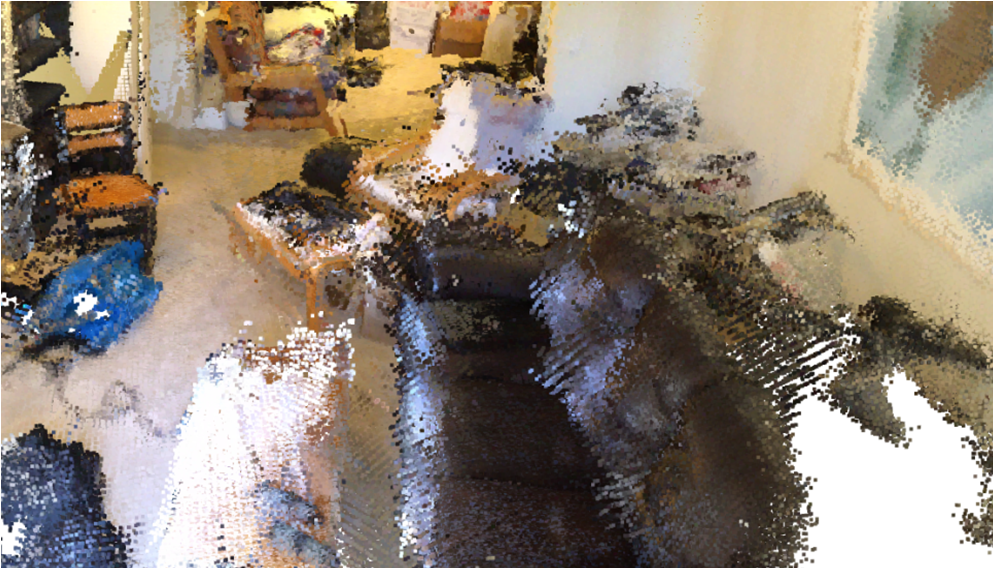
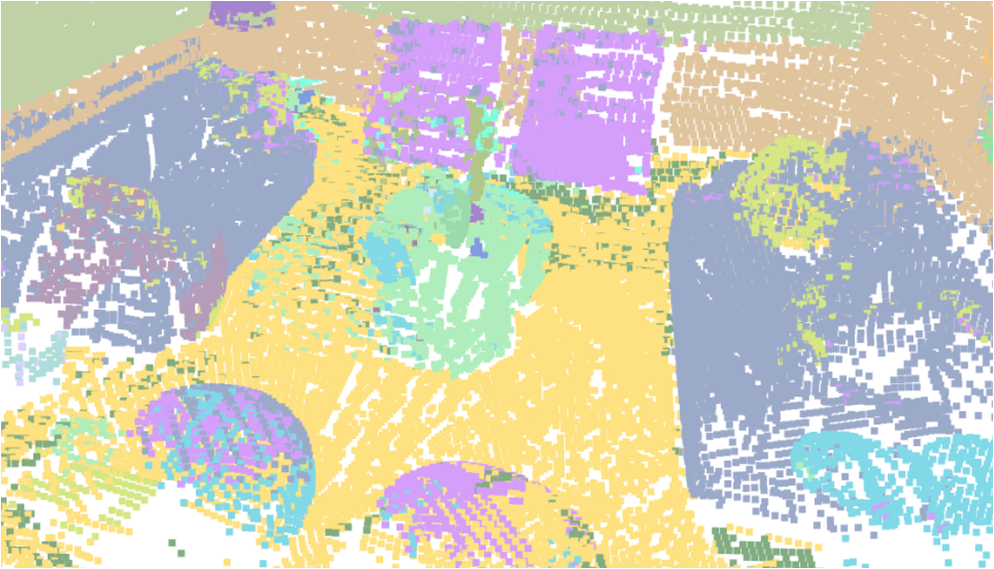
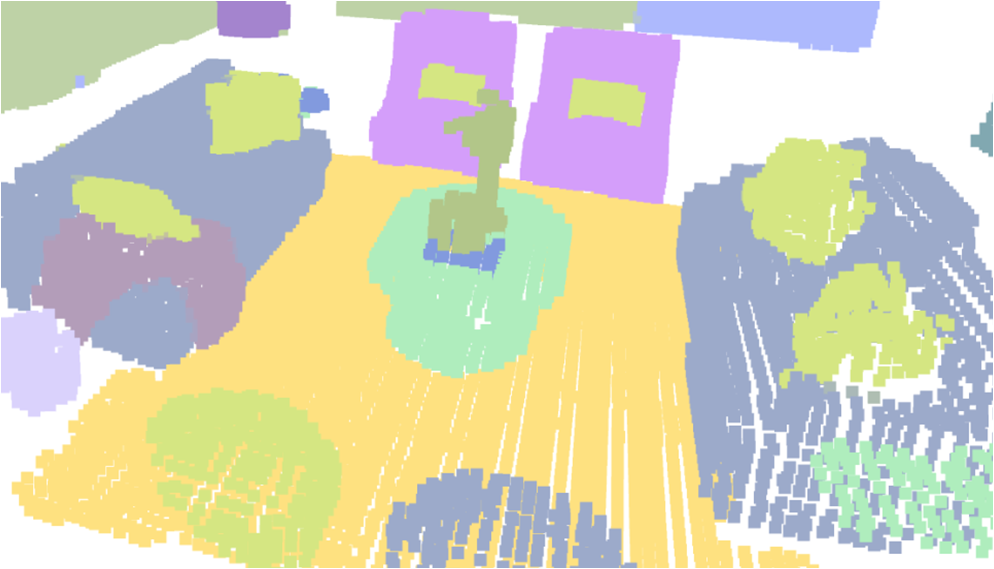
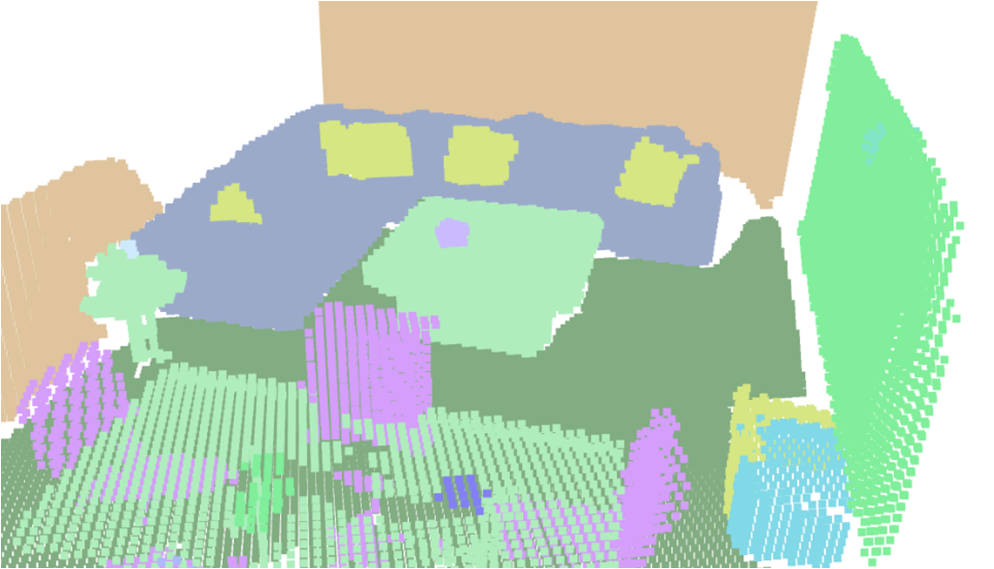
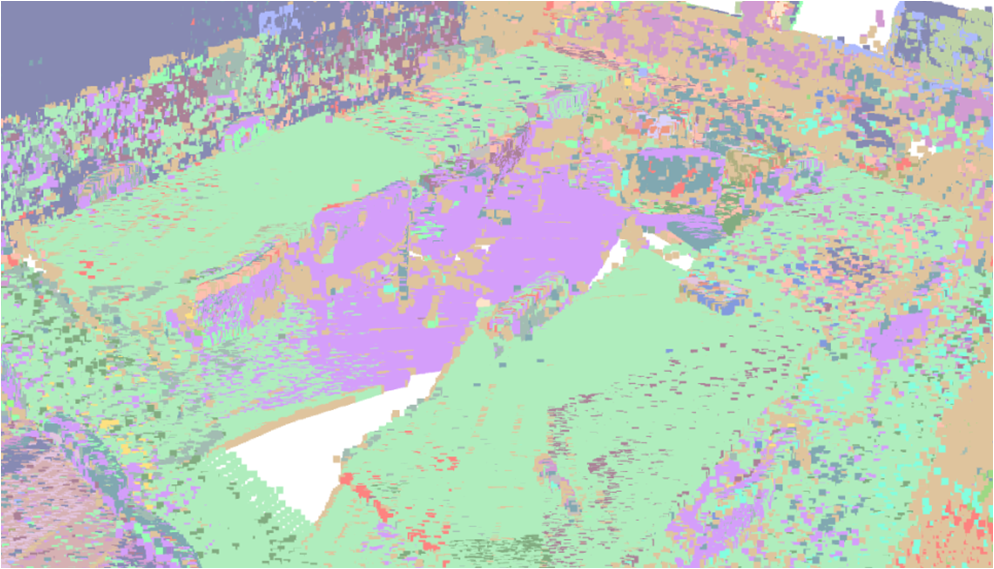
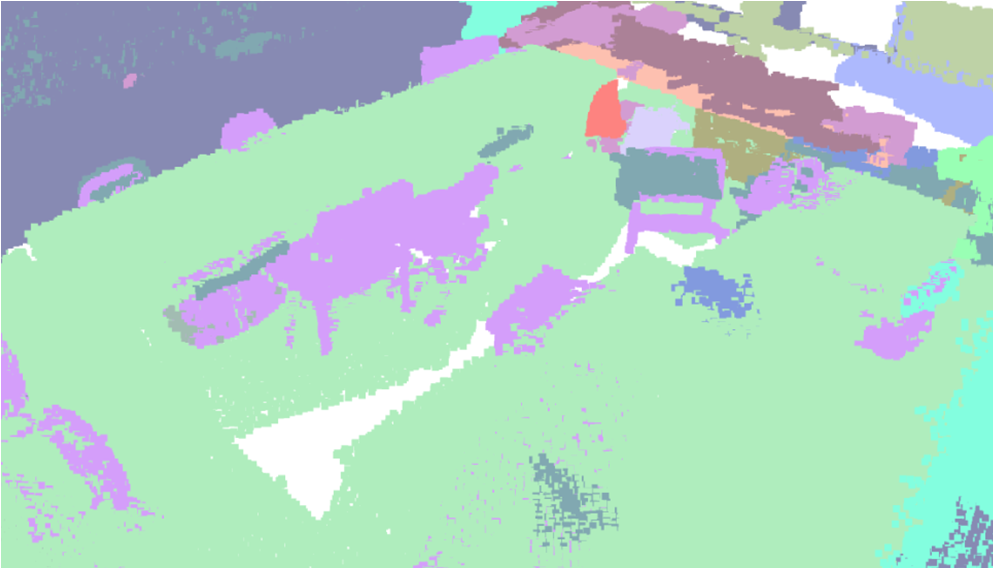
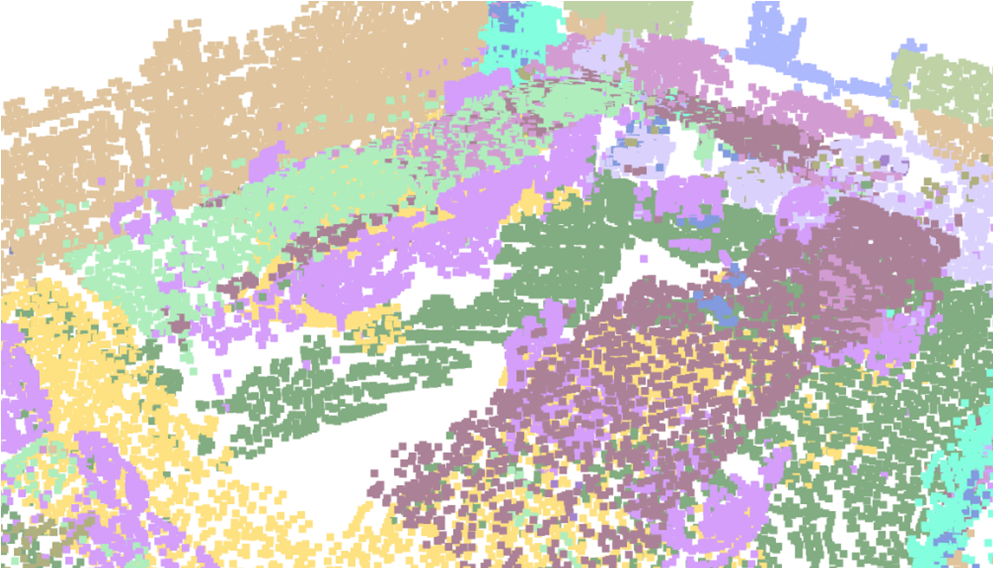
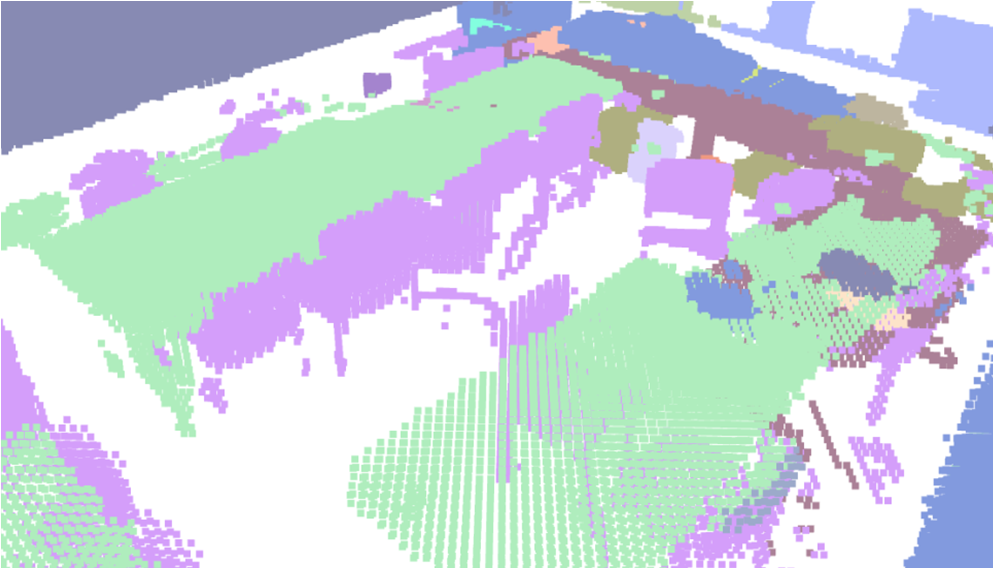
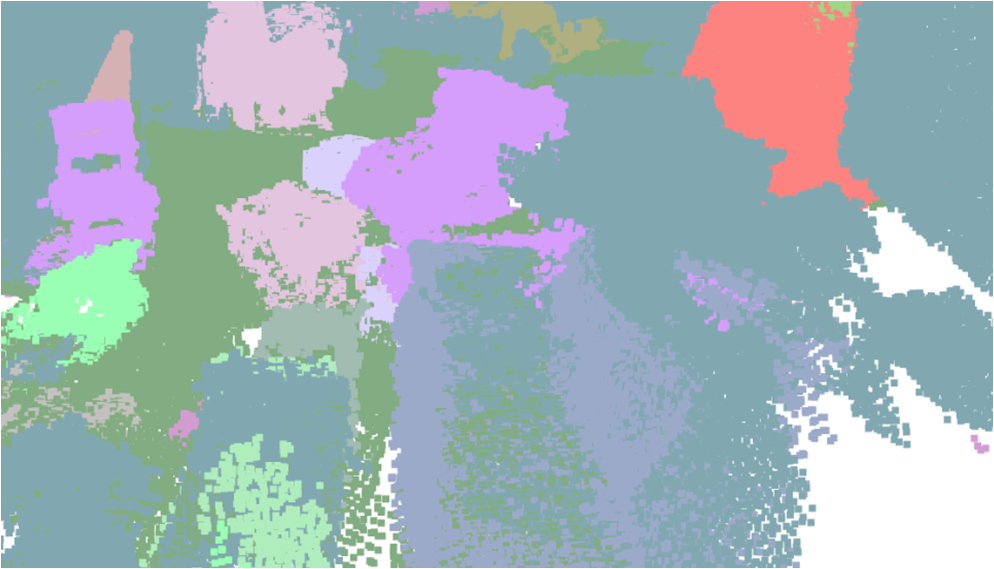
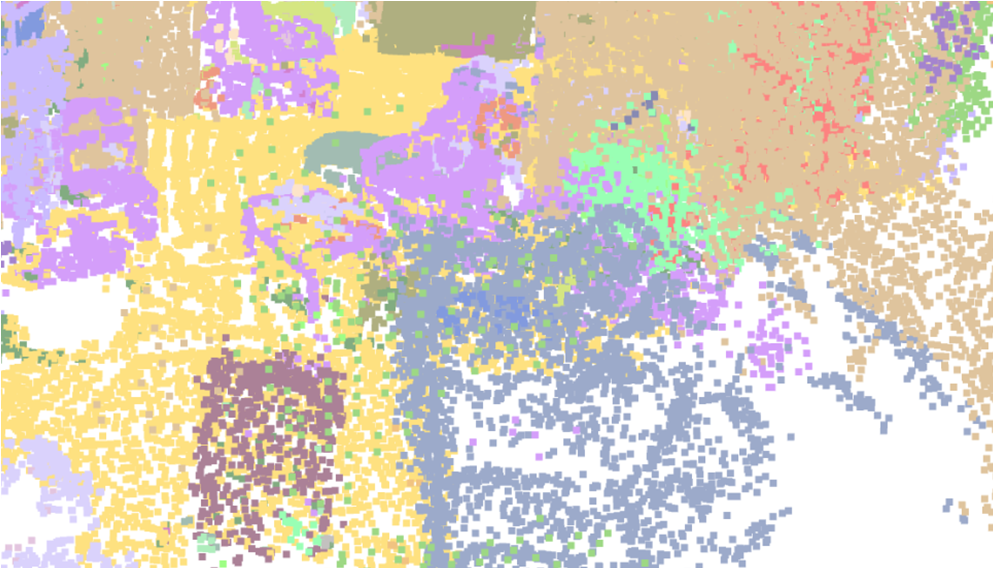
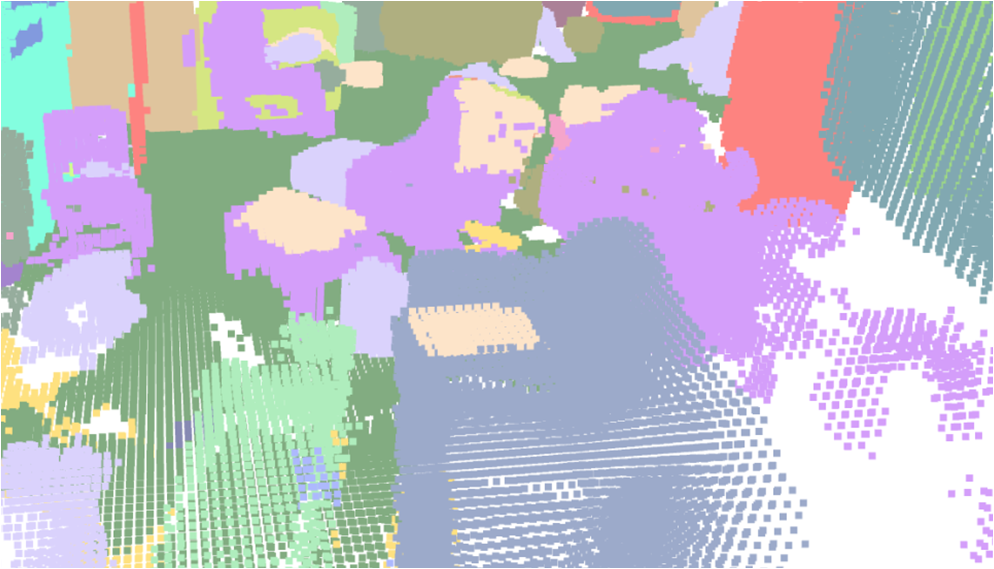
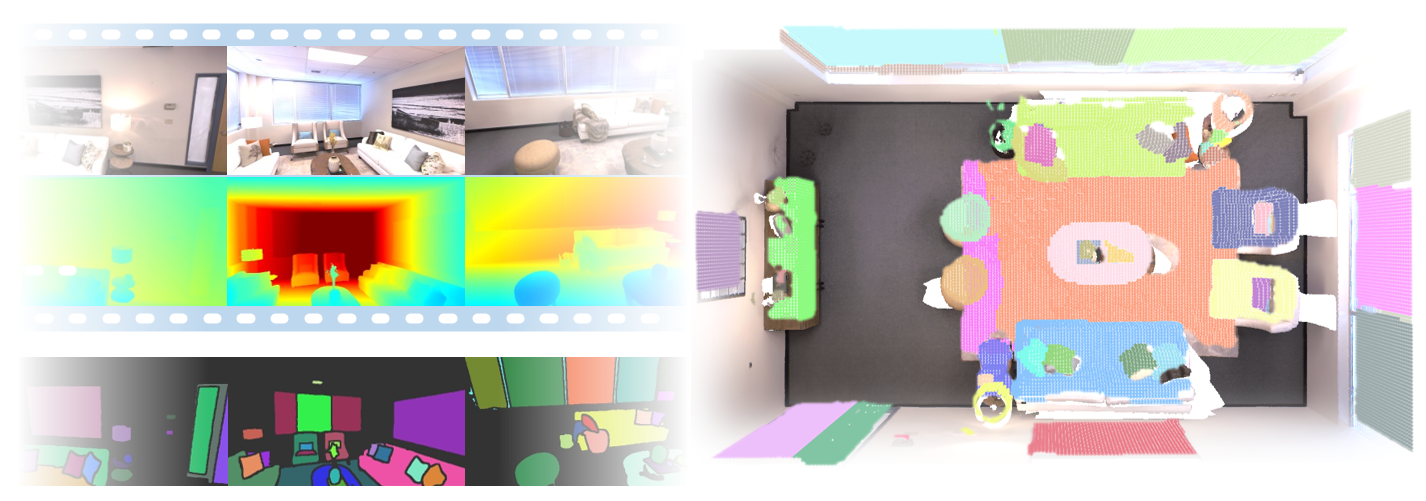
Visualisation of scene obtaind by different methods.
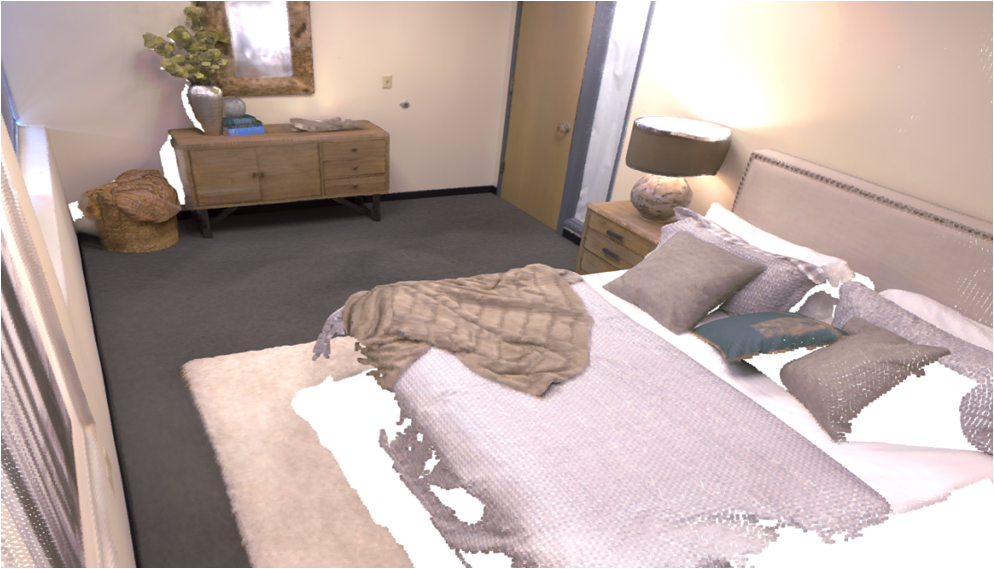
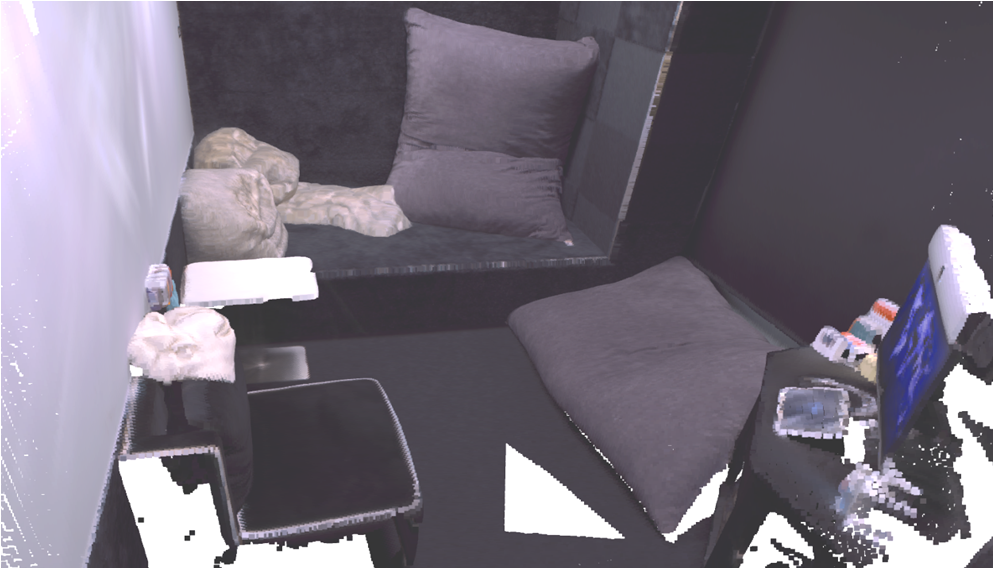
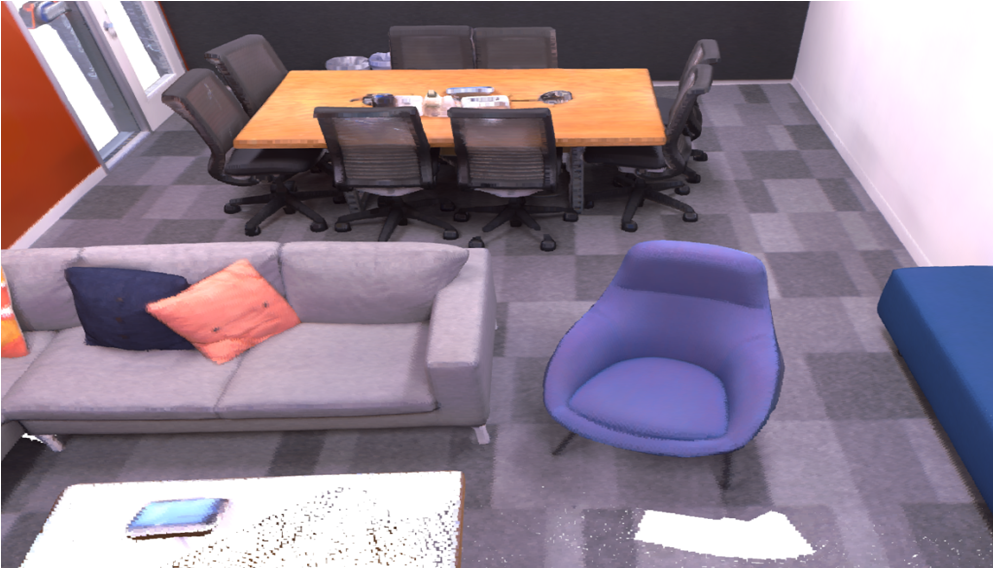
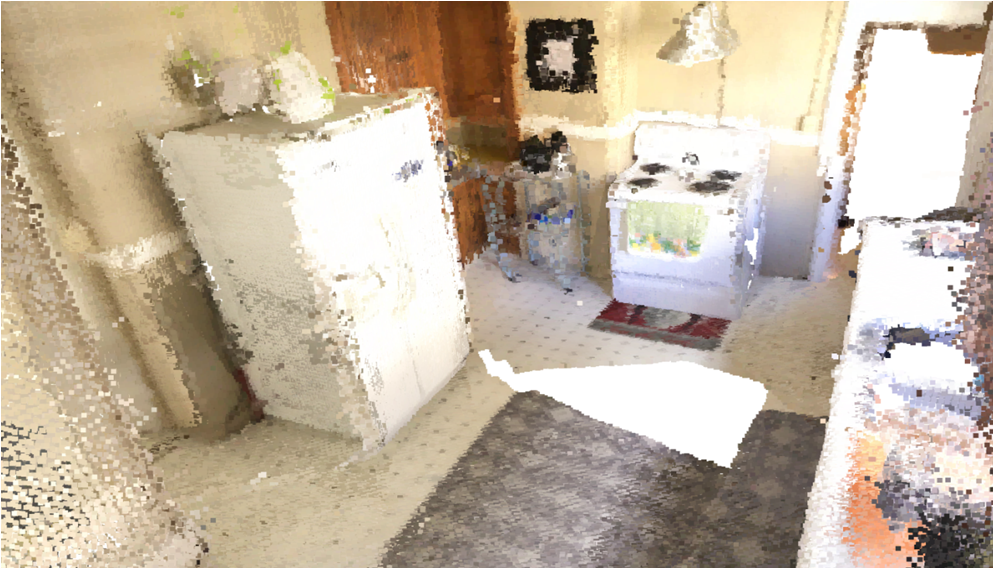
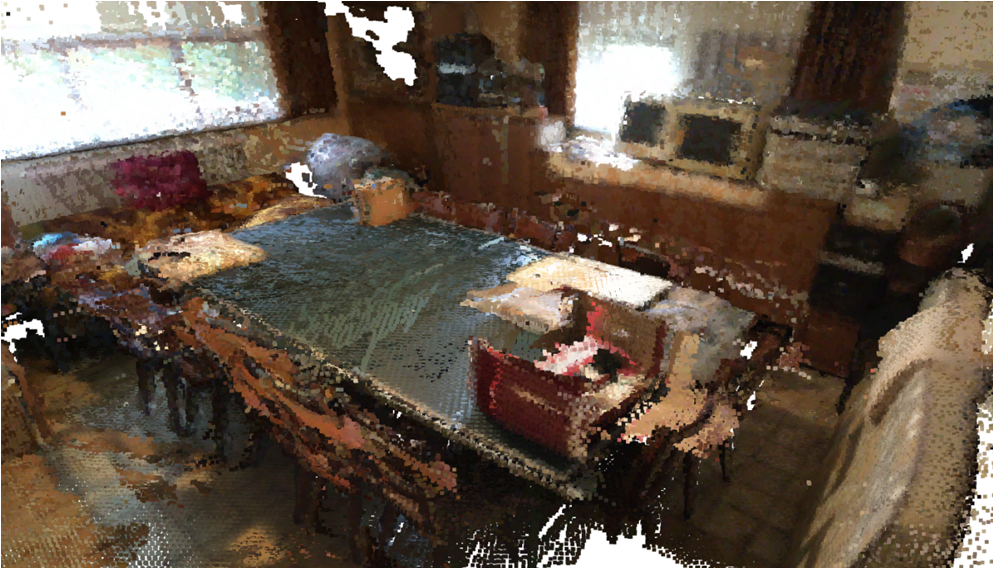
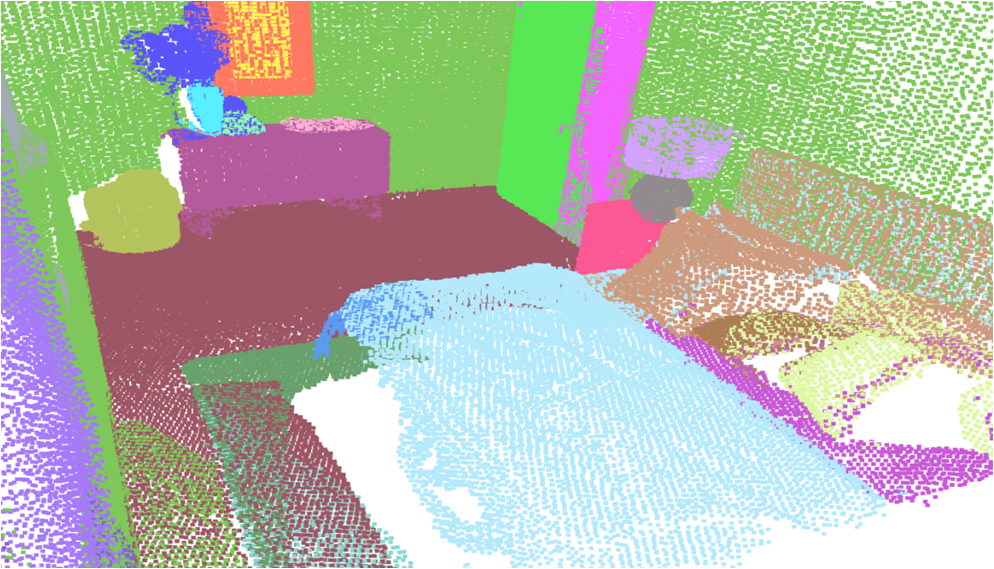
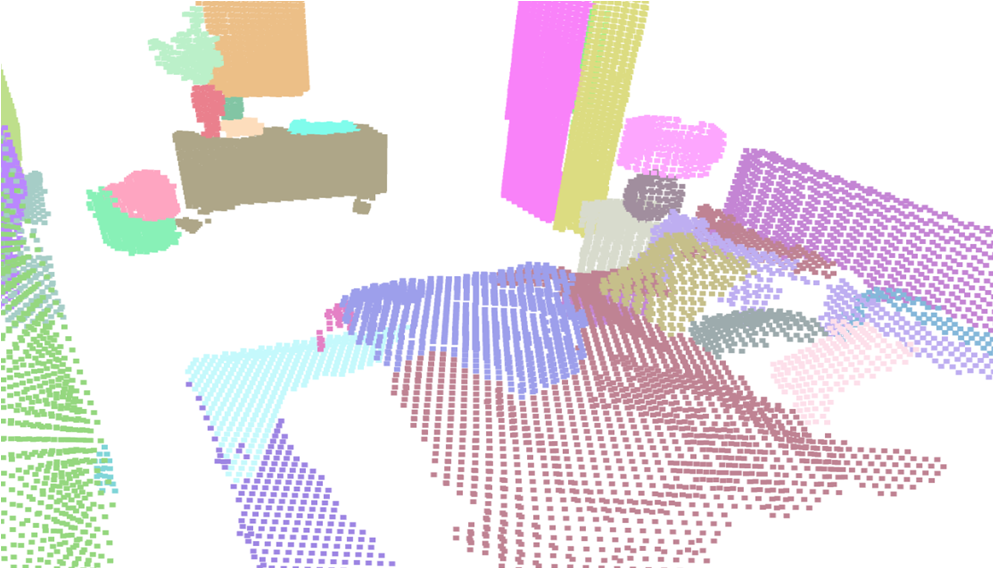

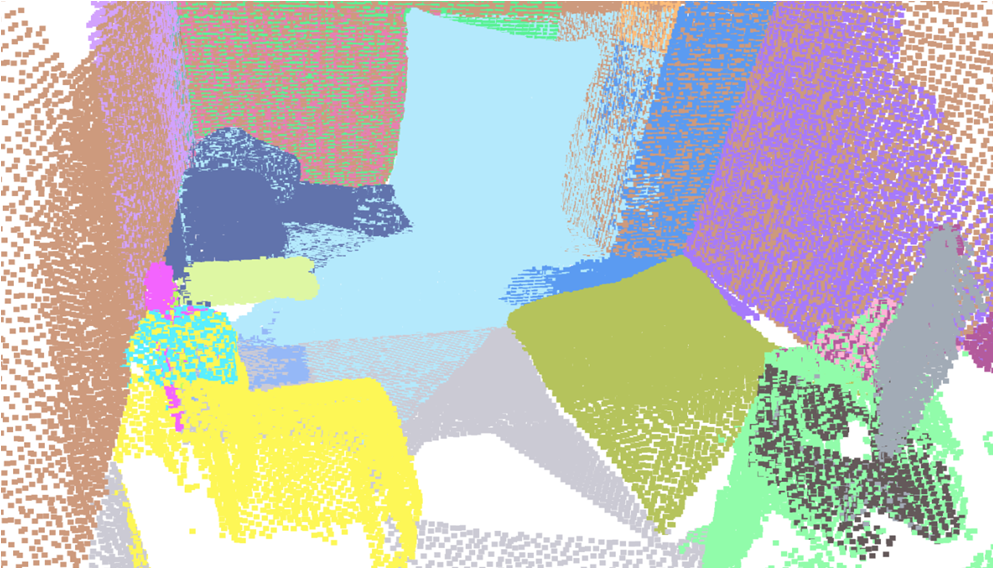
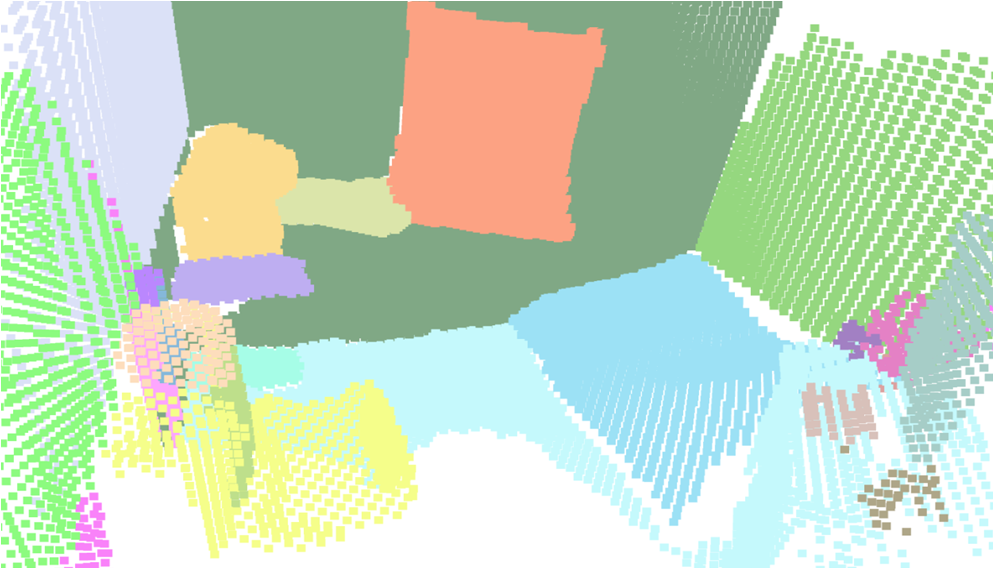

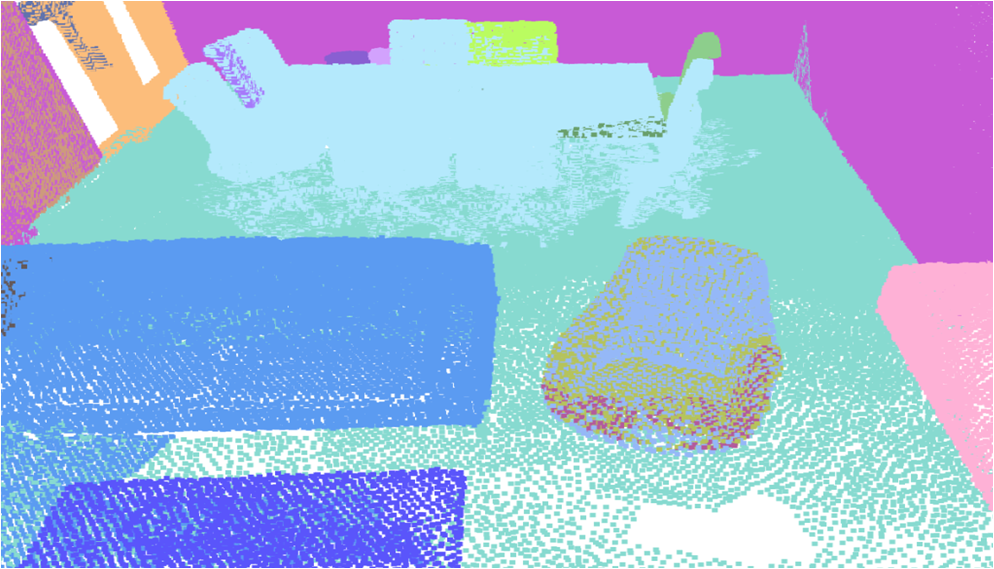
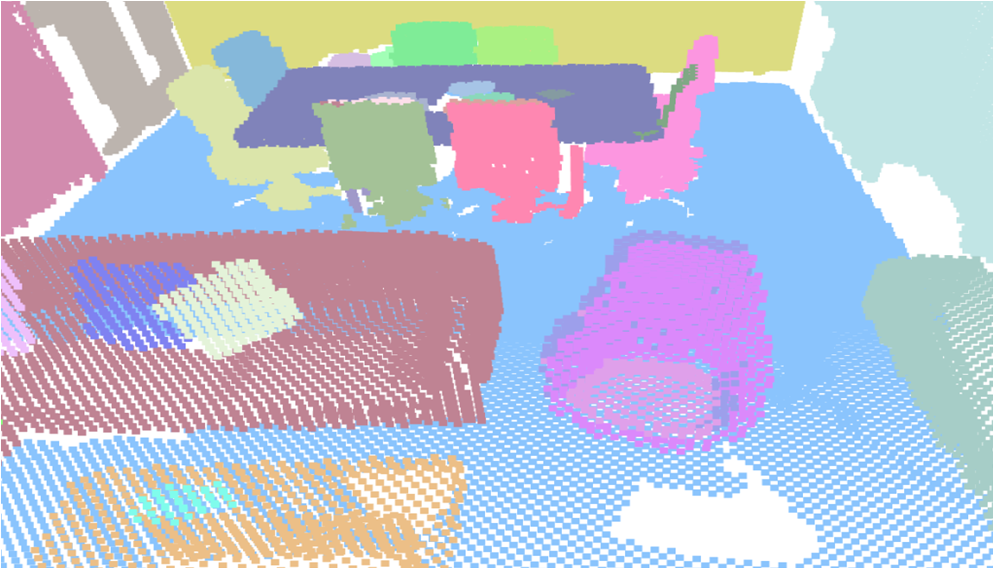

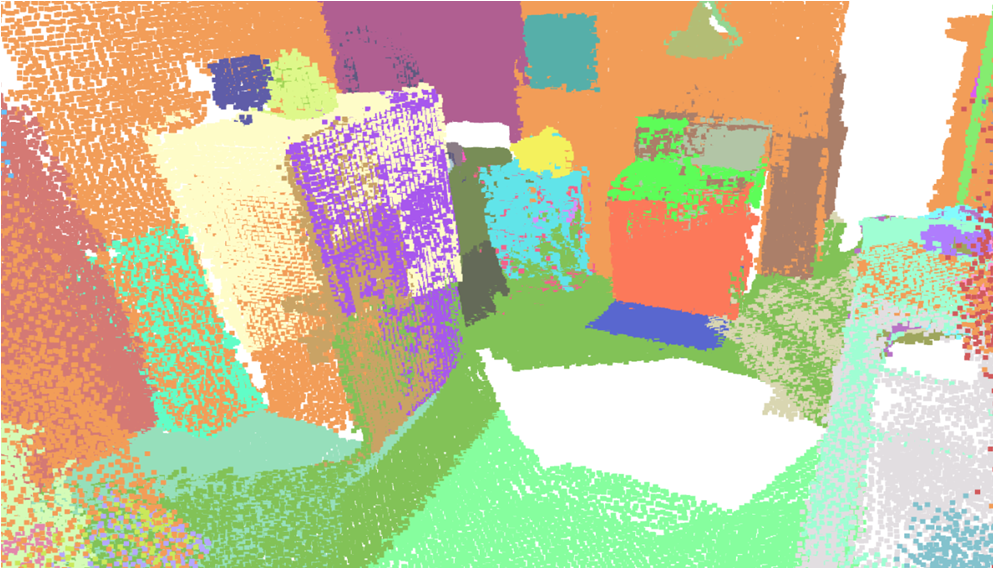
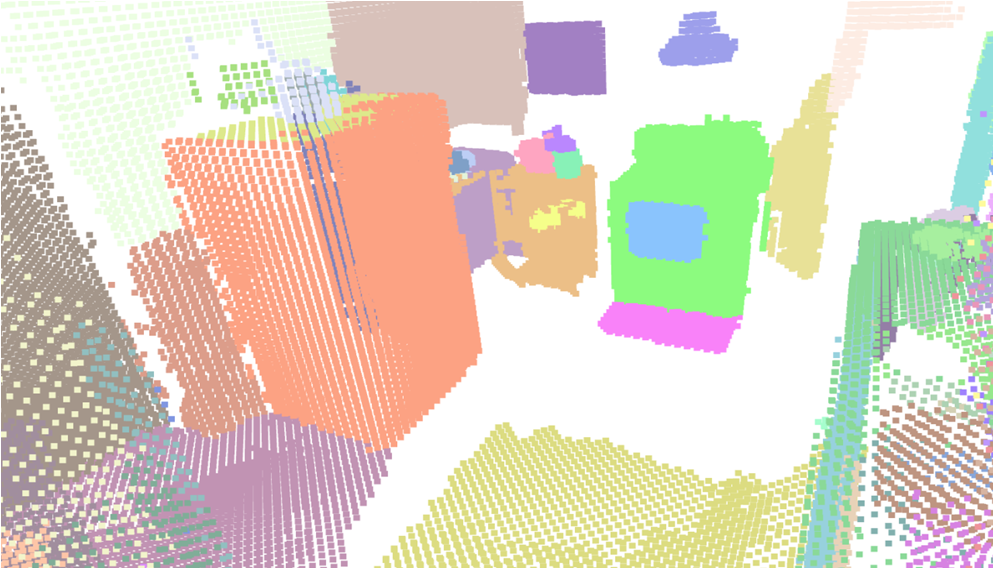

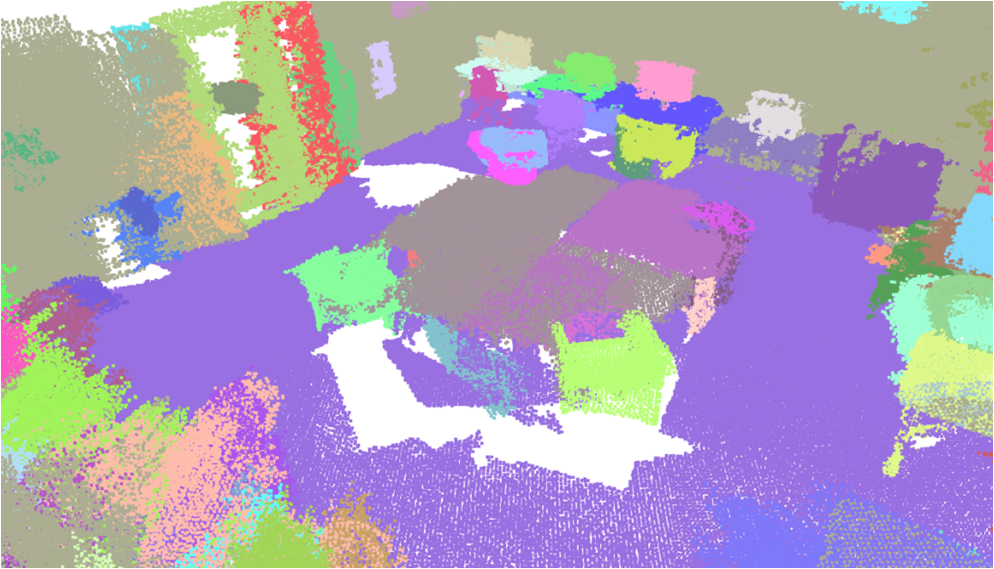
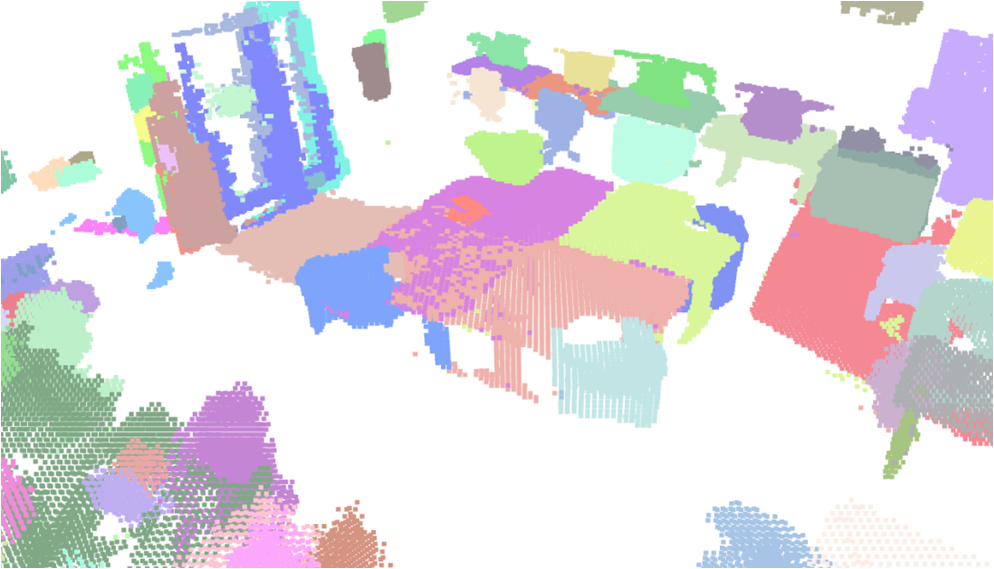
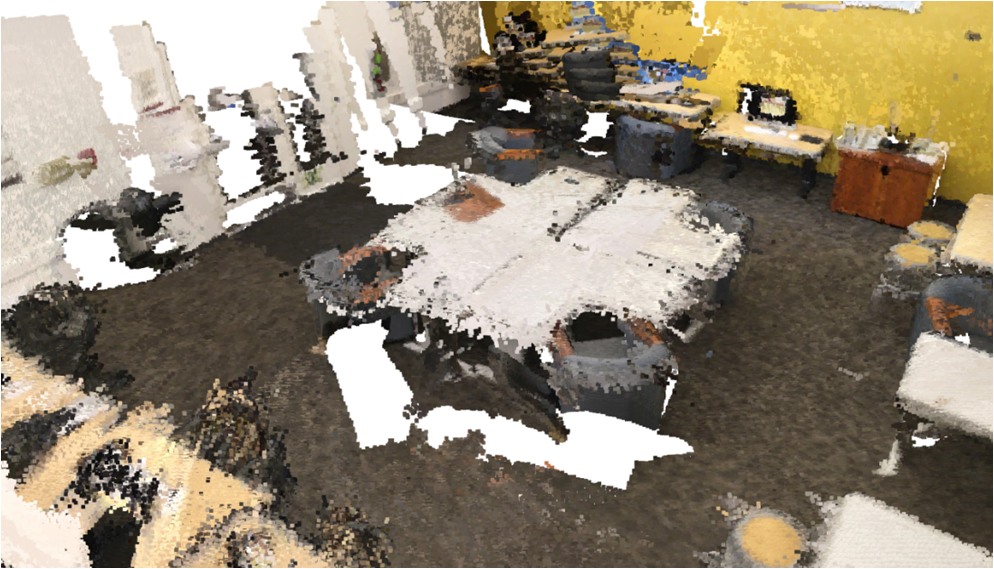
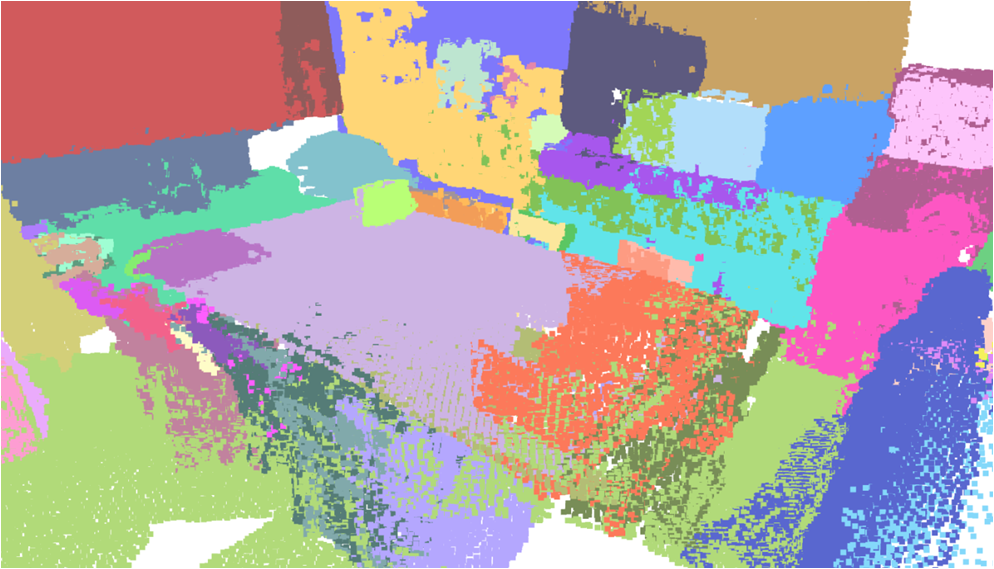
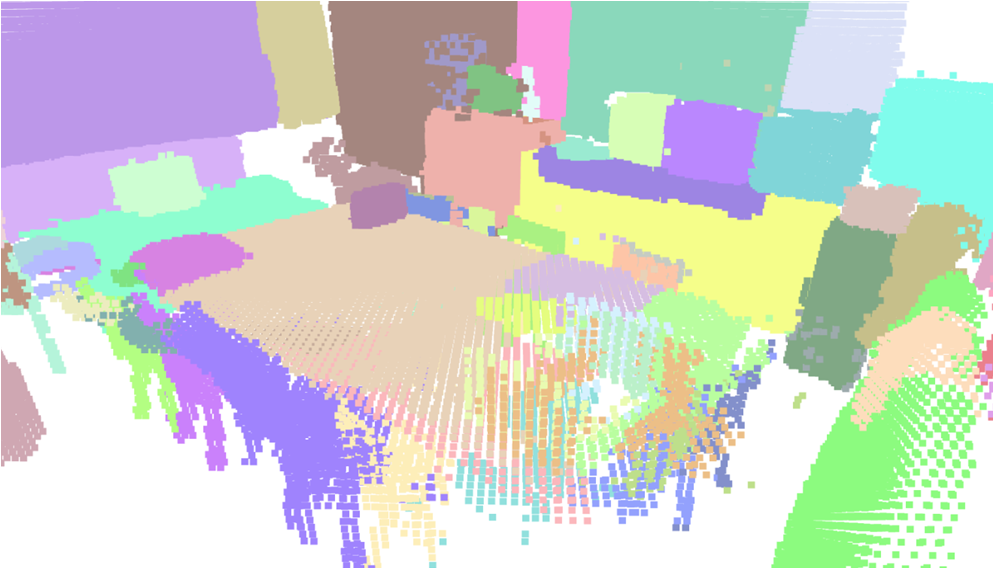

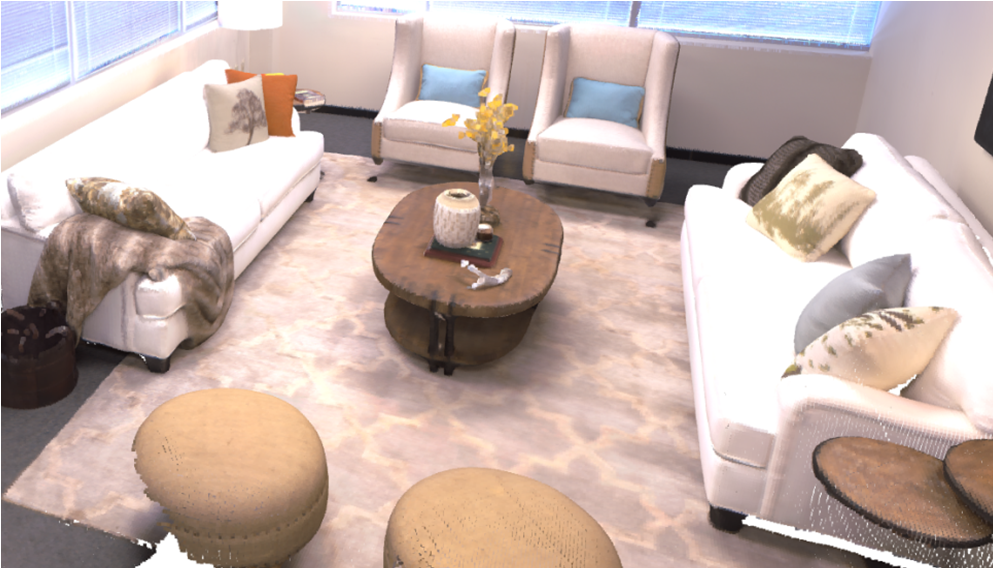
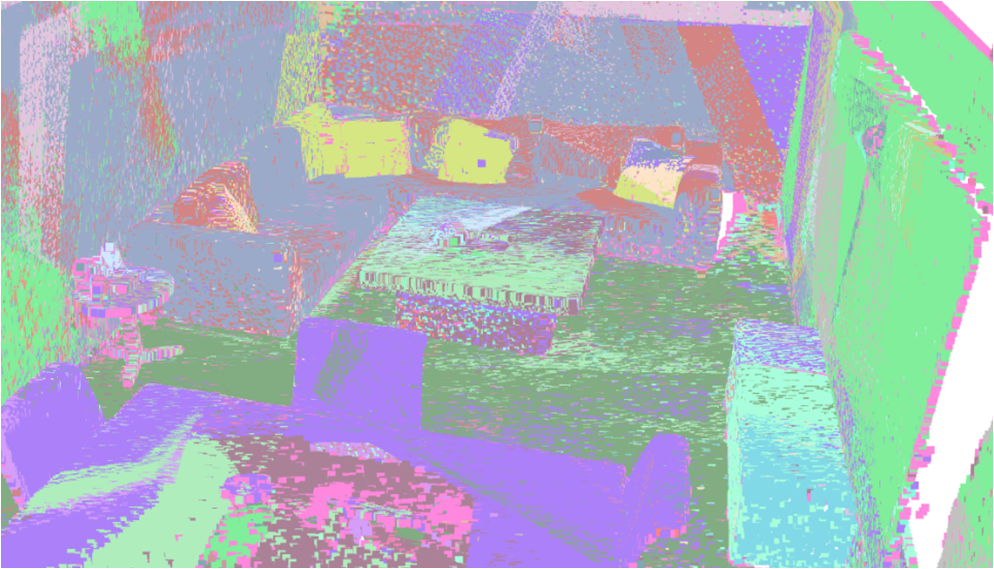
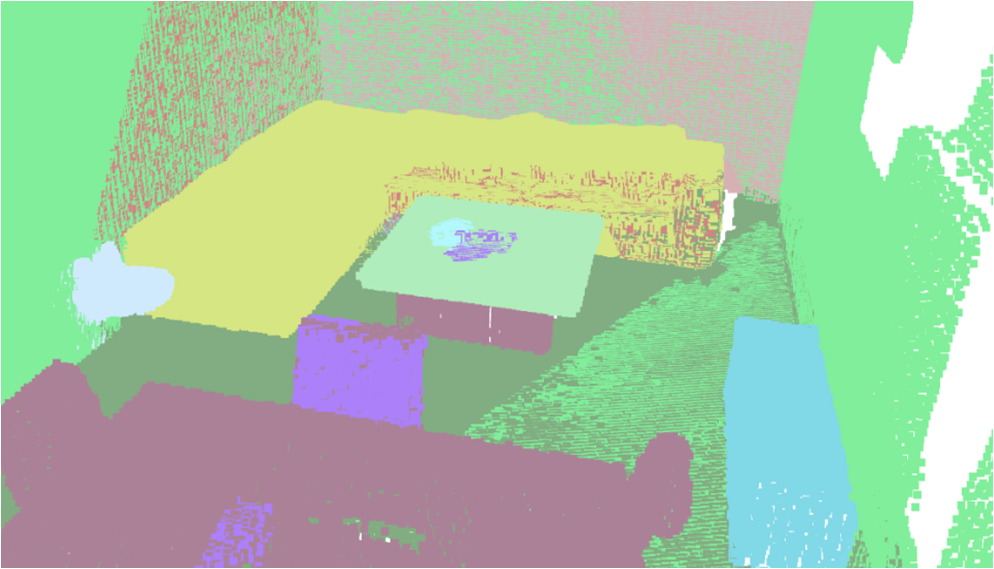
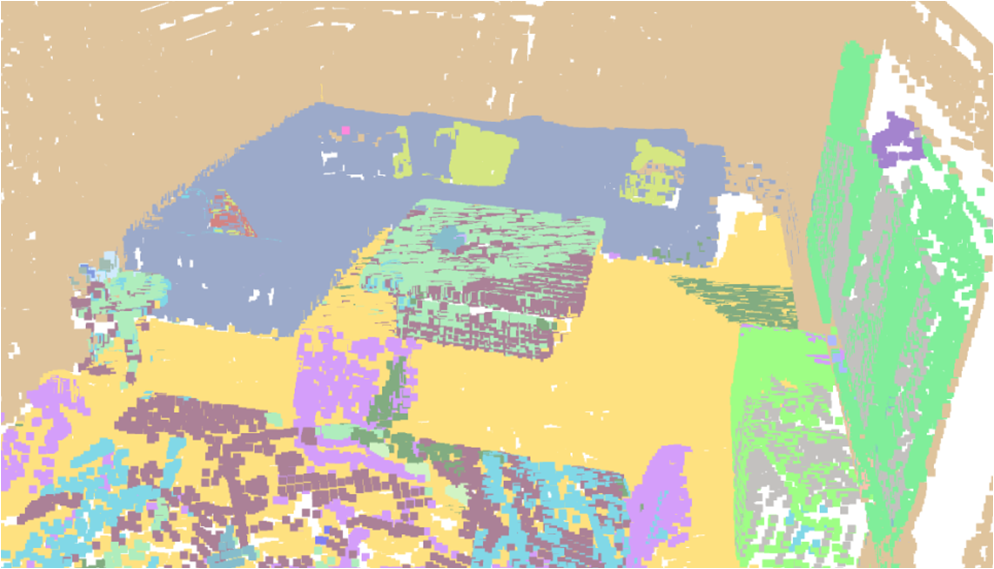
Visualisation of scene obtaind by different methods.